Styling
Bold, italics and underlining
We will now look at some simple text formatting commands.
Bold: Bold text in LaTeX is written with the
\textbf{...}command.Italics: Italicised text in LaTeX is written with the
\textit{...}command.Underline: Underlined text in LaTeX is written with the
\underline{...}command.
An example of each of these in action is shown below:
Some of the \textbf{greatest}
discoveries in \underline{science}
were made by \textbf{\textit{accident}}.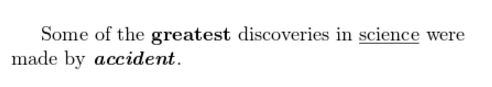
Another very useful command is the \emph{...} command. What the \emph command actually does with its argument depends on the context - inside normal text the emphasized text is italicized, but this behaviour is reversed if used inside an italicized text- see example below:

Moreover, some packages, e.g. Beamer, change the behaviour of \emph command.
Multiple Columns
Introduction
Two-column documents can be easily created by passing the parameter \twocolumn to the document class statement. If you need more flexibility in the column layout, or to create a document with multiple columns, the package multicol provides a set of commands for that. This article explains how use the multicol package, starting with this basic example:

To import the package, the line
is added to the preamble. Once the package is imported, the environment multicols can be used. The environment takes two parameters:
Number of columns. This parameter must be passed inside braces, and its value is 3 in the example.
"Header text", which is inserted in between square brackets. This is optional and will be displayed on top of the multicolumn text. Any LATEX command can be used here, except for floating elements such as figures and tables. In the example, the section title and a small paragraph are set here.
The text enclosed inside the tags \begin{multicols} and \end{multicols} is printed in multicolumn format.
Column separation
The column separation is determined by \columnsep. See the example below:

Here, the command \setlength{\columnsep}{1cm} sets the column separation to 1cm. See Lengths in LaTeX for a list of available units.
Unbalanced columns
In the default multicols environment the columns are balanced so each one contains the same amount of text. This default format can be changed by the stared environment multicols*:

If you open this example on Overleaf you'll see that the text is printed in a column till the end of the page is reached, then the in continues in the next column, and so on.
Inserting floating elements
Floating elements (tables and figures) can be inserted in a multicolumn document with wrapfig and wraptable.

Floats in the multicol package are poorly supported in the current version. Elements inserted with the conventional figure* and table* environments will show up only at the top or bottom of the next page after they are inserted, and will break the layout. The example presented here is a workaround, but you may expect some rough edges. For instance, if the float width is set to \linewidth it causes a weird text overlapping. This said, below is a brief description of the commands:
\usepackage{wrapfig}. Put this line in the preamble to import the package wrapfigThe environment
wrapfigurewill insert a figure wrapped in the text. For more information and further examples about this environment see Positioning images and tables.The environment
wraptibleis the equivalent to wrapfigure but for tables. See Positioning images and tables for more information.
Inserting vertical rulers
A vertical ruler can be inserted as column separator to may improve readability in some documents:

If you open this example on Overleaf you will see the column separator can be set to a specific colour also. Below a description of each command:\usepackage{color}.This line is inserted in the preamble to enable the use of several colours within the document.\setlength{\columnseprule}{1pt}This determines the width of the ruler to be used as column separator, it's set to 0 by default. In the example a column whose width is 1pt is printed.\def\columnseprulecolor{\color{blue}}The colour of the separator ruler is set to blue. See the article about using colours in LATEX for more information on colour manipulation.\columnbreakThis command inserts a column breakpoint. In this case, the behaviour of the text is different from what you may expect. The column break is inserted, then the paragraphs before the breakpoint are evenly distributed to fill all available space. In the example, the second paragraph is at the bottom of the column and a blank space is inserted in between the second and the first paragraphs.
Last updated
Was this helpful?